The Hand, Arm & Shoulder Specialists
since 1986
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Cubital Tunnel SyndromeUlnar Nerve Transposition/Decompression
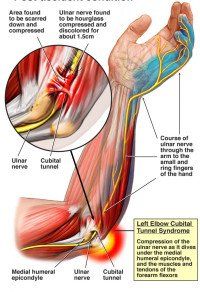
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome is a nerve compression injury in the elbow that involves the ulnar nerve. At the elbow joint, the ulnar nerve passes through a small passage called the Cubital Tunnel, located near the medial and posterior aspect of the elbow (an area which is commonly referred to as the “funny bone”). There are five different sites in this region that can cause compression of the nerve in the Cubital Tunnel. As the nerve becomes compressed or entrapped, it produces pain, discomfort, numbness, and decreased hand strength.
Most people are familiar with the odd sensations felt when accidentally bumping this area, as brief numbness, tingling and shooting pain occur. Similar symptoms are experienced in Cubital Tunnel Syndrome, but they are experienced on a chronic level. Symptoms are most intense along the ulnar (inside) aspect of the forearm, often extending down into the ring and small fingers.
If you exhibit symptoms of Cubital Tunnel Syndrome, you should promptly see your physician. Nerve testing may be prescribed to determine your level of compression. Your physician may also prescribe arm therapy to help alleviate the pain and improve function. Based on the severity of the condition, splinting, specific exercises, modalities, and other treatments can be initiated to assist in gliding the ulnar nerve and reducing compression to the area.
Surgery for Cubital Tunnel Syndrome is an option for those who do not respond conservative treatment. An ULNAR NERVE TRANSPOSITION may be performed to relocate the ulnar nerve away from its compression point to enable healing, pain relief, and greater freedom. Following surgery, a comprehensive arm therapy program will normally be prescribed to assist you in regaining range of motion, strength, and function in the affected arm.
MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The information contained in this website is intended for informational and educational purposes only. You should always with your physician for the diagnosis and treatment of any injury or condition. The content on this web site is general in nature and not complete, and it should never be used for diagnostic or treatment purposes.
Useful links
Contact Info
OAK BROOK630.572.6301630.572.6314 Fax2803 Butterfield Rd, Suite 350Oak Brook, IL 60523info@KleiserTherapy.com
NAPERVILLE NORTH / AURORA
630.236.7630630.548.5590 Fax504 North Route 59, Suite 124Naperville, IL 60563info@KleiserTherapy.com
LEMONT630.257.0211630.257.0290 Fax1217 State Street, Suite BLemont, IL 60439info@KleiserTherapy.com
2803 Butterfield Rd, Suite 350
Oak Brook, IL 60523
info@KleiserTherapy.com
NAPERVILLE NORTH / AURORA
630.236.7630
630.548.5590 Fax
504 North Route 59, Suite 124
Naperville, IL 60563
info@KleiserTherapy.com
LEMONT
630.257.0211
630.257.0290 Fax
1217 State Street, Suite B
Lemont, IL 60439
info@KleiserTherapy.com